Evolution and History of Human Resource Management
Evolution and History of Human Resource Management: Over the period of time, it is important to understand the evolution of Human Resource Management to get know about their functions, practices and philosophy of the HRM that are being used in different circumstances. A development pattern of management is followed by Human Resource Management due to the similar types of problems existed in both the fields.
Also See: 15 Challenges of Human Resource Management
HRM is a popular term that is considered for handling the manpower of an organization in a very efficient and effective manner. Still, HRM is becoming an amalgamation of organizational behavior, personnel management, legislation of labour and industrial relations. Let us learn today, evolution and history of Human Resource Management (HRM).
Also See: Mba Hr Project Topics
Evolution and History of Human Resource Management
Here, we have jotted down the brief points of discussion that are significant in the evolution of human resource management. Let us begin.
Historical Perspective of Human Resource Management
The term “Human Resource Management” is originated currently and used from the year 1980s. The production and manufacturing of goods are only done with the help of skilled artisans and craftsmen in ancient times. All the equipment that is needed for the production of the articles owned by these artists and they sold these artists by themselves in the marketplace.
So, the employee & employer and even master-servant did not arise in all such cases. The entire affairs of goods and services are managed by these artists and with the help of family members. On the contrary, the apprentice, as well as a certain category of hired staff, is used by some of the effluent craftsmen. It established a close relationship between the apprentices and the craftsmen, moreover, they kept an eye over all related operations with their apprentices and family members.
Also See: Scope of Human Resource Management: Complete Reference
A human approach was evolved in their relationship and after a long period of training, some apprentices opened their own enterprises and others worked with their master to get extra benefits. Guilds are formed by the skilled craftsmen during the medieval period to protect their trade. These involved slaves, serfs and laborers. To get a proper understanding of Human Resource Management, it is pretty relevant to the treatment and management of slaves, serfs and labourers.
1. Managing slaves
In most of the ancient civilization, an important source of manpower was Slaves as they can be sold as well as purchased the commodities. The wealthy rulers, landlords, chiefs as well as businessmen purchased commodities from these slaves and control the slaves at a very great extent.
Moreover, they also use them for other tough works such as carrying loads, construction in buildings and rowing ships and boats and so on. In return, they gave them shelter and food. In this way, they were keeping an eye over the slaves and manage them.
Also See: 20 Objectives of Human Resource Management
2. Handling Serfs
In feudal societies, the serfdom was widely prevalent and in the pre and early medieval period. Serfs were doing the agricultural work of their landlord and associated activities. A piece of land gave by the landlords so that they can earn their bread and butter. The lords were handling serfs on the basis of the principle of authoritarianism and there was a reliable relationship between the feudal lords and serfs.
3. Managing Indentured Labor
With the emergence of mercantilism and advancements in the industrial sector, there was the presence of the indentured labour system. Due to an increase in the demand for goods and various commodities, the demand for labour increases and the same was fulfilled by people who are migrating from remote areas to industrial towns.
Also See: Standard Causal Model Of HRM: Definition, Features, Process
The management of labour is different from that of serfs as well as slaves. This indentured labour was abode by the terms and conditions to work for an employer and not with anyone else.
Various Eras in the evolution of Human Resource Management: From the 19th century to till today
Different stages are there in the evolution of Human Resource Management for its growth from the industrial era to the present era. These are categorized as follows:
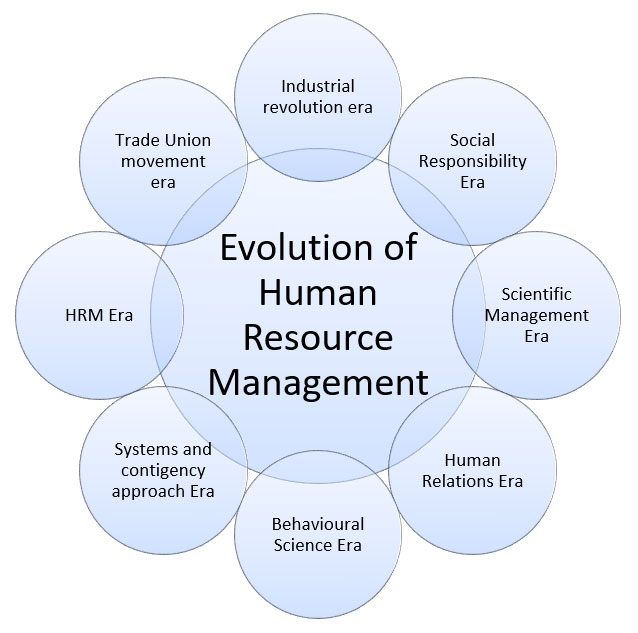
Industrial revolution era (19th century)
During the advancements in the industrial sector in Western Europe and the USA, there was a systematic growth of HRM. The industrial revolution comprises of the development of machinery, usage of mechanical energy and the existence of the concept of the factory with ample manpower.
The old cottage system was replaced by the factory system. Under this system, there were various changes introduced such as the mechanical process, migration of workers from their place to other places and communication between the workers and the owners. Three systems of HRM were introduced under this system such as the hiring of workers, training and controlling them properly. The master-servant philosophy was used to keep control over these workers.
Also See: 21 Vital Importance of HRM(Human Resource Management)
Trade Union Movement Era (Close to the 19th century)
With the emergence of the factory system, the workers started to establish their own union on the basis of their common interest which was named as Trade Unions. The basic aim behind these associations was to protect the interest of the members and deal with the grievances of the workers that may arise due to child labour, long hours of work and pathetic working conditions.
Other working issues also became prevalent such as economic issues, fewer wages, worker’s benefits and other services. To give a backfire to these problems, the Trade Union did strikes, slowdowns, walkouts, boycott and so on as their underlined weapon. All these issues reflected the need for employee Grievance handling system, disciplinary practices; expand the benefits of employees, holidays and vacation time and defensible structure for a wage.
Social Responsibility Era (beginning of the 20th century)
A humanistic, as well as paternalistic approach, was adopted towards the factory workers by the first decade of the 20th century. At the short note, it signifies that the worker is like a child for their owner and the owner is the father who took care of the entire labour.
Some additional facilities and concessions are given to the labour by the industrialists who were working on this policy such minimize the hours of working, improved working conditions, shelters to workers and so on. This is a social approach that was adopted to combat the problem of workers and it is considered as a welfare scheme to control the workers.
Scientific Management Era (1900-1920s)
Taylor started looking for some technical approaches to increase the worker’s productivity at the beginning of the 20th century. He wrote some of the scientific techniques that are relevant to manage the workforce and even a book on management as well. The management of the workers is relevant to the scientific management techniques such as functional foremanship, standardization and simplification of work and differential wage rate system.
Some of the principles of scientific management are given below:
- Replacement of rule of thumb with science.
- Not conflicts but only harmony.
- Cooperation and say no to individualism.
- Growth of each worker.
Human Relations Era (1930-1950s)
More focus was put on the human factor at work and what affected the people’s behaviour during the 1920’s. During this era, it was highly recommended to use psychology while doing personnel testing, interviewing, attitude measurement as well as learning also.
Basically, the period was defined as “Industrial Psychological Era” in the year 1924. After conducted deep research by the professors of Harvard Business School, it was observed that the productivity of the workers depends on social factors at work, formation and influence of groups, the nature of leadership and supervision and at last, the communication.
It was concluded that the management ought to maintain human relations at work along with physical conditions to increase productivity.
Behavioral Science Era (1950-1960s)
On the contrary to the happy workers are good workers, the behavioural scientists suggesting that the behaviour of a human be the highlighted aspect. Various research methodologies are used to comprehend the nature of the job as well as people in the working atmosphere.
Here are some of the major conclusions made by the behavioural scientist that are given below:
- People like their work but there is a need to establish some goals so that they can work properly to achieve them in a timely manner. It also increases their job satisfaction.
- Employees generate maximum creativity as compared to how much it is needed. But their potential is not utilized in a good manner.
- Usage of the untapped potential of an employee is the duty of managers.
- An environment ought to be created so that people can contribute in the best possible way and this must be done by the manager.
- The expansion of subordinate’s influence, self-direction and self- control can improve the operating efficiency.
Also See: 12 Responsibilities And Role of HR Manager
Systems and Contingency Approach Era (1960 onwards)
In the present era, a high level of attention is seeking by the System and Contingency Approach Era. It is a cooperated approach that signifies the empirical data to manage the human resources. It is attached with a huge idea of analyzing the objects that must depend on the analysis involving simultaneous variables that are mutually dependent on each other.
Human Resource Management Era (1980 onwards)
A huge number of people started working in factories when there was a replacement of the old cottage system with the factory system. Then, there was a need for hiring, developing and keeping an eye over the workers. With this intention, the department of industrial relations emerged in most of the big business firms.
By the time, the scope of the industrial relations department was extended as the conflicts arose between the supervisory staff too. Then, it was renamed as Personnel department.
With the increasing competition within the business sector, the competition for talent, skills, abilities and knowledge also touched the sky and it reflected the need for the good human management team. Further, the manpower was considered as socio-psychological beings for the achievement of organizational goals, not as physiological beings. It changed the nomenclature of the personnel department and sheds light on the Human Resource Department.
Also See: Functions of Human Resource Management
Bottom Line
With the sway of all these advancements in the area of Human Resource Department, the largest professional association also changed the name from American Society for Personnel Administration to the Society for Human Resource Management in the year 1990. In addition to this, the academic studies named as “Personnel Management” also converted to “Human Resource Management”. Now, the department of Human Resource is of great value for any organization whether it is big or small.
So it was all about Evolution and History of Human Resource Management. If you liked it then please comment below.
Good work.
Please I need your references.
Can you send to my email?
simonimoh1@gmail.com.
Thanks
Send me other historical era and example
we will try to find if it exists….
Hello, did you find referances?
thanks for the comment…reference is wiki and shrm
Very informative!
May I ask for your references? Thank you so much for the information.
thanks for the comment…reference is wiki and shrm
my reference is https://101hrm.com
I’m so glad I saw this .After reading about 3 to 4 articles,I now understand it just by reading yours .
thanks bro
I need a reference can you send me my email please
Good work, Detailed and informative
thanks